How To Design Your Own Kitchen Garden
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(584) : eval()'d code on line 3
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(584) : eval()'d code on line 3
The estimated reading time is 9 minutes
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(115) : eval()'d code on line 3
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(115) : eval()'d code on line 3
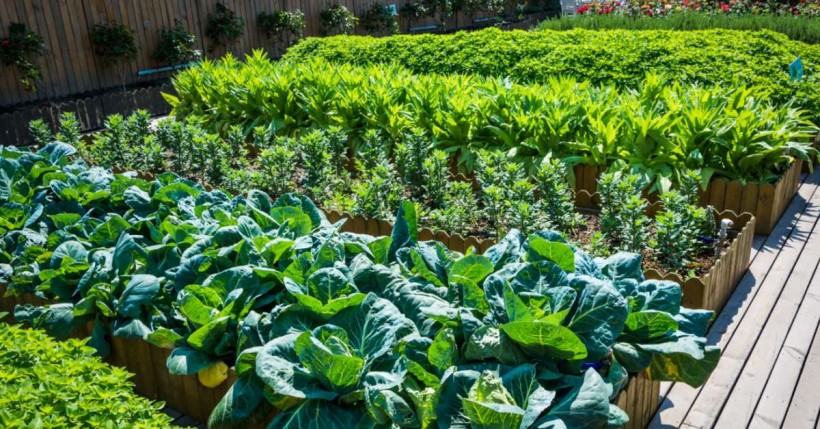

If you’re interested in gardening, kitchen gardening is the perfect choice for you. There’s nothing better than the satisfaction of eating healthy and delicious fruits, vegetables, and herbs are grown in your own backyard.
Kitchen gardens have started growing in popularity. They’re appearing in backyards worldwide, and people simply adore them.
As kitchen gardens are becoming more and more popular, I often get this question: “What are kitchen gardens? Why are they called “kitchen gardens”?” So, to avoid any confusion regarding kitchen gardens, let’s explain what exactly a kitchen garden is.
What Are Kitchen Gardens?
Kitchen gardens, also known as potager, are gardens that are used for growing fruits, vegetables, herbs, and flowers. The French have been intermixing these plants in their potagers, or kitchen gardens, for hundreds of years. A kitchen garden is situated on private land very close to the house, and it is separated from the lawn area. In this way, it’s close to a water source, and harvesting is made more convenient.
Plants grown in kitchen gardens are free of chemicals and pesticides. Some people also add companion flowers to their kitchen garden which serve to repel pests and stimulate pollination.
What Differentiates A Kitchen Garden From A Vegetable Garden?
There are four main differences between these two types of gardens:
-
Location
Since vegetable gardens require more space and can sometimes get messy, they’re typically situated further from the dwelling. On the other hand, a kitchen garden is located near your house, and it also serves as a place where you and your family or friends can gather.
-
Size
Compared to vegetable gardens, which require a larger area of land, kitchen gardens are typically smaller.
-
Purpose
Vegetable gardens are developed with the intention of gathering huge harvests and growing large quantities of food that can be canned or preserved. This is not the case with kitchen gardens. These gardens are designed with the aim of learning something new, watching plants grow, having fun, and creating a healthy lifestyle. It’s all about the experience that kitchen gardens can offer you.
-
Aesthetics
Kitchen gardens usually consist of raised beds that are symmetrically organized and have a pleasant appearance.
Vegetable gardens, on the other hand, are usually organized in straight rows with muddy gaps popping up in places where fruits or veggies have been dug up.
-
Tending
Kitchen gardens are tended more often. For example, you may pay your kitchen garden a visit several times a week to pick fresh veggies or herbs to prepare meals. On the other hand, vegetable gardens require intense tending, which involves big planting and getting in large harvests.
How To Design A Kitchen Garden
-
First Things First, Choose The Right Time To Create Your Kitchen Garden
The best time to start designing your kitchen garden is early spring. Determine what size the plot you’d like to be. Keep in mind that a large kitchen garden requires a considerable amount of preparation, hard work, and maintenance.
-
Decide Where You Want To Position Your Kitchen Garden
What plants you’ll grow depends on the light levels and how much space you can provide each plant with. Read the labels on the seed packets to see how much space and light each plant will require and then choose appropriate containers and pots.
To make sure your fruit and vegetable plants produce well, you need to:
- Plant your fruits and vegetables in a sunny spot where they’ll be exposed to bright, direct sunlight, preferably six to eight hours a day. Keep in mind that some plants, such as raspberries, cherries, blackcurrants, and blackberries, can grow in shade.
- Protect your plants from harsh, drying winds.
- Provide your plants with compost-enriched soil.
-
Decide What Fruits And Vegetables You Want To Grow
To narrow your selection, make a list of all the types of fruit and vegetables you’d like to grow, and then check if you have the appropriate growing conditions.
If you’re an amateur, set clear and attainable goals. You’ll probably want to grow all the seeds available at your local garden center, but when you have little or no experience, this can be hard, almost impossible. In what follows, we’ve presented various types of plants you can grow in your kitchen garden. Here they are:
- Fruits: Strawberries, currants, blueberry bushes, gooseberries, apple, and pear trees.
- Vegetables: Red cabbage leaves, early potatoes, onions, tomatoes, cucumbers, sweet peppers, hot pepper plants, carrots, beetroot, eggplant, and broad beans.
- Herbs: Basil, thyme, oregano, mint, rosemary, and sage.
- Colourful flowers: Marigolds, columbines, gladiolus, poppies, geranium, hollyhocks, and sweet peas. (1)
-
Make A Plan For Getting The Best Results From Your Garden
- Grow plants that produce high yields.
- Grow plants that don’t require a lot of space, such as tomatoes.
- Grow salad leaves.
- Choose plants that are expensive to buy or which are not always available in supermarkets, such as Swiss chard, thyme, rosemary, mint, and sage.
-
Prepare The Soil
It’s best to check the pH levels of the soil in your kitchen garden so that you can choose crops that suit it.
Then, you should remove all the weeds or turf and dig over the soil. Next, you should put clear plastic sheeting over the soil surface where you intend to plant your vegetables for a few weeks to warm up the soil. This will also kill off weeds.
The next thing you should do is enrich the soil with compost, leaf mold, or well-rotted manure. The organic matter will help the soil preserve nutrients and moisture. However, regardless of what type of organic matter you’ll choose to enrich your soil with, make sure it suits it.
In addition, keep in mind that there can be different soils within your garden, and adding organic matter can benefit all types of soil. Good soil is one that is crumbly, aerated, and loose and that can absorb water and drain well. (2)
-
Design A Kitchen Garden In Raised Beds
If you intend to grow small plots of vegetables, know that raised beds are perfect for this. Raised beds increase the temperature of the soil, have good drainage, and prevent the soil from compacting. They also protect the soil from heavy rain, hinder pathway weed growth, and act as pest repellent.
If you think that making raised beds on your own is time-consuming, you can buy ones in your local garden centers.
-
Choose The Layout Of Your Kitchen Garden
How you’ll decide to layout your kitchen garden depends on your needs and how much space you can provide. One useful tip for organizing a kitchen garden is to separate the land where you intend to grow vegetables into three parts:
- One for herbs and salads
- One for root vegetables
- One for peas and beans
You can also allocate one section to mixed vegetables, such as cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, and eggplant.
Separating your plot into three or four parts is important since you can’t sow the same crop in the same soil in two successive years.
In addition, it is recommended that you mix fruit, vegetables, flowers, and herbs since the mix of various plants and ornamentals confuses pests.
-
Create Access Pathways
Create access pathways so that you can easily approach the garden beds for planting, weeding, and harvesting as well as spot and get rid of any pests.
You can also try using vertical gardening ideas. For example, you can grow cucumbers and peas up frames.
-
Grow Plants From Seed In Your Kitchen Garden
You can sow seeds in your garden when there’s no longer any risk of frost, and the soil is 7 degrees Celsius at the minimum – seeds can’t grow in temperatures below 7°C. You can also put plastic sheeting over the soil to warm it up, but it’s easier to begin growing your plants indoors. You can sow seeds in pots and containers and place them on a bright window sill. Once your seedlings grow and get strong and there’s no risk of frost, you can plant them out.
Vegetables, such as carrots, potatoes, peas, and onions, can be sown under cloches in February, whereas salads and Swiss chard can be grown year around.
Other plants which are easy to grow include strawberries, beets, onions, tomatoes, and garlic.
How To Care For Your Kitchen Garden
- Weeding A Kitchen Garden
To prevent weeds from invading your garden beds, add a few inches of mulch over the soil when you’ve finished planting your seedlings. In this way, your vegetables will be able to grow freely, and you’ll need to do less weeding work.
- Watering A Kitchen Garden
Most vegetable crops require moist soil, so you’ll need to water your vegetables well once a weak. Container-grown vegetables require more frequent watering. If your soil isn’t good for holding water, add sand to improve it. To increase water retention, you can also mulch garden beds with compost, manure, or leaves. But, make sure the mulch doesn’t touch the plants.
Conclusion
- A kitchen garden is used for growing fruits, vegetables, herbs, and flowers.
- Plants grown in kitchen gardens are organic, healthy, and free of chemicals.
- Compared with vegetable gardens, kitchen gardens are located closer to your house, they’re smaller, they aren’t created with the aim of gathering huge harvests, they are more symmetrically organized, and they don’t require intense tending.
- To design a kitchen garden, you need to follow these steps:
- Choose the right time to create your kitchen garden
- Decide where you want to put your kitchen garden
- Decide what type of plants you want to grow
- Make a plan for getting the best results from your kitchen garden
- Prepare the soil in your kitchen garden
- Design a kitchen garden in raised beds
- Choose the layout of your kitchen garden
- Create access pathways
- Grow plants from seed
- Kitchen gardens require thorough watering and weeding.