All You Need to Know About Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(584) : eval()'d code on line 3
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(584) : eval()'d code on line 3
The estimated reading time is 3 minutes
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(115) : eval()'d code on line 3
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/dietofli/public_html/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(115) : eval()'d code on line 3
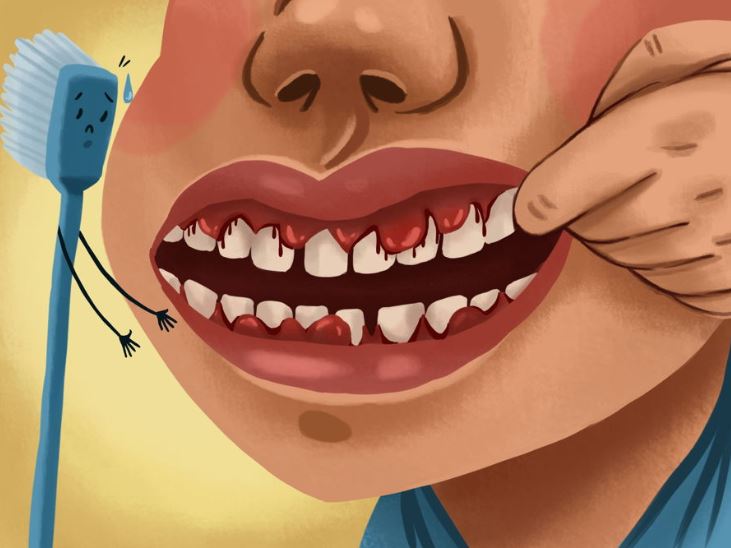
Gum disease is a common condition that may affect both children and adults. Most adults experience it at least once. Gum disease may lead to bad breath or bleeding gums. The early phase of gum disease is known as gingivitis. Everett gum disease should be treated early to avoid periodontitis.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease occurs when there is a build-up of plaque. The plaque has bacteria that may be harmful to your gums. Brushing your teeth regularly may help get rid of plaque. If one does not brush their teeth, the plaque build-up may affect the health of their gums. It can cause soreness, bleeding, and swelling. (1)
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Oral hygiene is usually enough to treat mild cases of gum disease. Proper hygiene includes brushing your teeth twice a day and flushing regularly. Regular dental check-ups may help you get rid of plaque or tartar.
The good dentist gives their patients tips to clean their teeth and prevent the build-up of plaque. In the case of extreme gum disease, dental and medical treatment may be necessary. Some patients may need surgery.
You should see a dentist if you notice any signs of gum disease. They will carry out a dental exam to examine the health of your gums. A periodontal probe is often used for the examination. Some dentists may use x-rays to check the health of your jaw bone and teeth.
The Difference between Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis is also known as gum inflammation. It comes before periodontitis. If not treated, gingivitis may progress to periodontitis.
Gingivitis happens when there is plaque build-up. The build-up may lead to inflammation and bleeding especially when you brush your teeth. With gingivitis, the gums may be irritated but your teeth remain firm in their sockets. The damage caused by gingivitis is reversible.
Periodontitis occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. It affects the inner layer of the gums and causes bone to pull away from the teeth.
The space remaining between the gums and teeth leads to the collection of debris which may lead to infection. The body will release enzymes as it attempts to fight bacteria and prevent the spread of plaque.
Poisons that are produced by the bacteria in plaque and the body's enzymes break down the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place. As the disease gets worse, the pockets become deeper and a lot of gum tissue and bone are destroyed. The teeth can no longer be held in place. They become loose and may start to fall out. (2)
Causes of Gum Disease
The main cause of gum disease is plaque. However, there are other things that may lead to periodontal disease. Some of them include the following;
- Hormonal changes
- Illnesses such as diabetes, HIV, and cancer
- Poor oral hygiene
- Family history of dental problems
- Smoking
- Medication that may affect oral hygiene
Perfect Smiles Dentistry in Everett may help you treat any type of gum disease. It is committed to providing you with personalized and comprehensive dental care. Perfect Smiles Dentistry offers preventive, general, and cosmetic dental services for patients of all ages.
Since the treatment plans are personalized, the dentists can make sure that the care you get works for your lifestyle and needs with minimal inconvenience. Contact them today and book your appointment. (3)